Recently, Green Radar SOC observed a notable surge in sophisticated phishing schemes using Google redirect URLs to bypass traditional email gateways. These links exploit Google’s trusted domain to evade reputation-based filters. Additionally, layered redirects add complexity, making it challenging for both users and security systems to trace the final destination of the links.
Below is one of the scenarios to show how it works:
- Deceptive Email: A user received an email pretending a normal Microsoft 365 password expiration notification
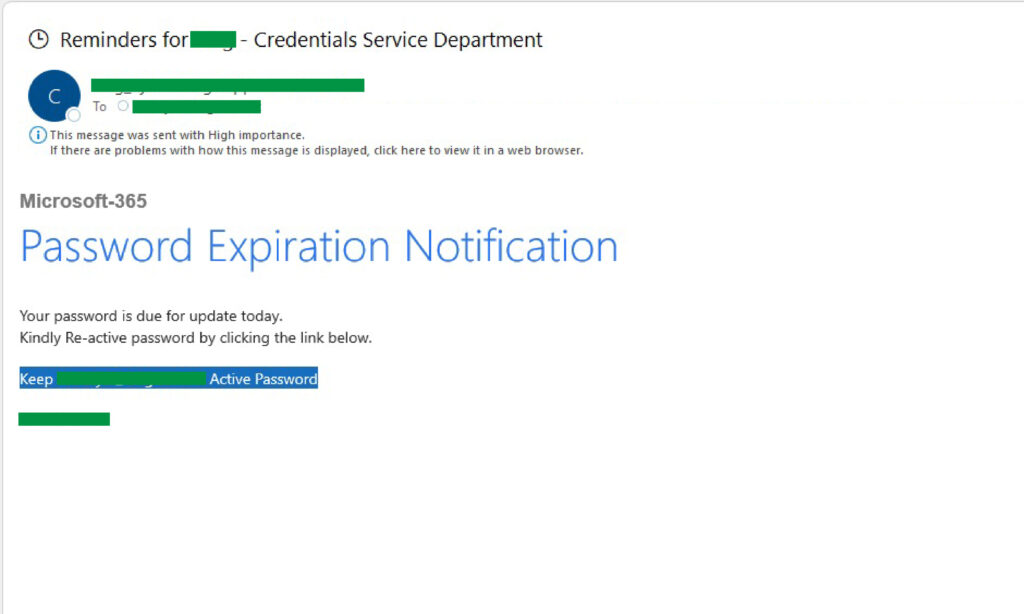
- Complex Redirects: The link contains multiple layers of Google redirect URLs. Upon clicking the link, users are redirected through these layers.

- reCAPTCHA Disguise: The initial Google link redirects to a seemingly harmless reCAPTCHA protection URL before ultimately leading to a malicious phishing site. This chain makes it harder for security gateways to detect the threat, and increase the likelihood that users will trust the domain.

- Credential Theft: The final phishing site prompts users to log in, aiming to steal their sensitive credentials.
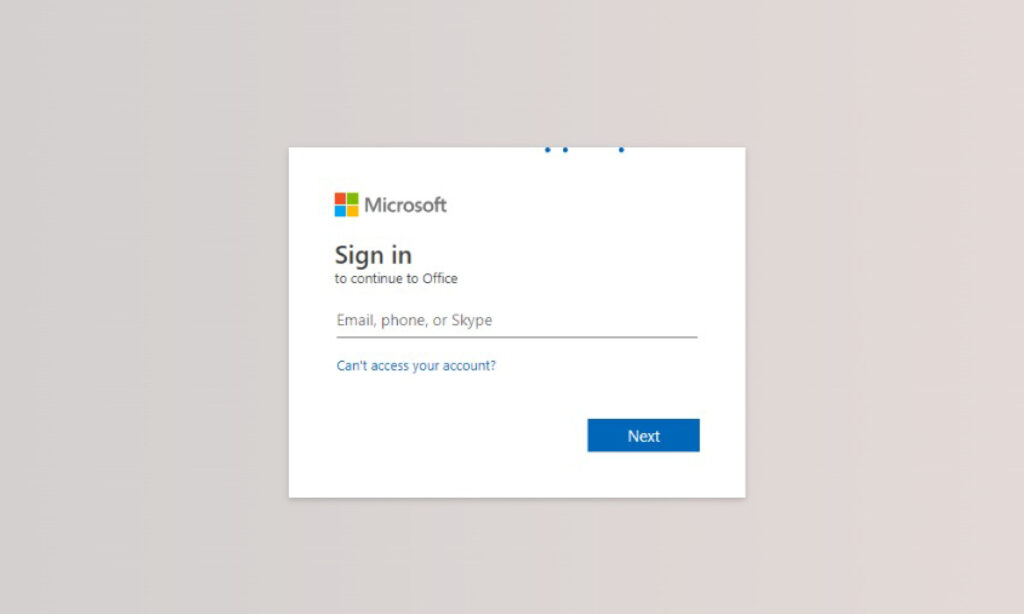
Conclusion:
Detecting redirections can be challenging to a user, as initial URL may appear authentic. Cyber threats are constantly evolving, making it essential for organizations to maintain high vigilance. By understanding sophisticated techniques like multi-layer Google redirect phishing, staying informed, and implementing robust security measures, we can better protect ourselves and our systems from potential breaches.
